ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES
- Those activities which generates some income are known as economic activities
- Sectors are groups of people who engage in diverse activities including the production of commodities or services.
Division of Economic activities. Three SECTORS of economy
PRIMARY SECTOR – related to farming activities
SECONDARY SECTOR – related to manufacturing
TERTIARY SECTOR – provide support to other two sectors
1. Primary Sector: The primary sector is when we make a product by extracting and collecting from nature.
2. Secondary Sector/ Industrial sector- This includes the transformation of natural goods into new forms through various manufacturing processes. Ex. Cloths from cotton, Sugar from sugarcane
3. Tertiary Sector / Service Sector – which helps in the development of primary and tertiary sector. Ex. Banking, Transport, Teachers,
Historical changes in sectors
1. The primary sector was the most important sector of economic activity in a country throughout its early phases of development.
2. With the innovation in farming methods, agriculture sector began to produced much more food than before.
3. People started working in industries, some involved in transportation.
4. Gradually, secondary sector became the most important in economy and providing employment.
5. Different industries related to food processing, equipment's making, textiles coming in large numbers.
6. This leads to start of services such as banking, health, education etc.
7. The service sector became the most important sector in terms of total production and started employing more people.
NOTE: - All sectors are interdependent on each other as the good and services produced in one is used in the other sector
- Goods and services are of two types
1. Final goods and services – goods and services that are directly consumed by the consumers.
2. Intermediate goods and services- good and services that are used for production and processing.
GDP – GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT
- GDP stands for Gross Domestic Product.
- GDP is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year
- The value of final goods and services produces in each sector during a particular year = total production of the sector
How to calculate GDP?
- Economists suggest that : the value of product and services should be used rather than adding up the actual numbers(Quantity).
- Every goods and services and intermediate goods are not calculated.
- Only the value of final goods and services should be counted (A+B+C)
Q. Why only the value of final good are calculated?
Only final goods and services are counted, to avoid multiple counting, since their prices covers the cost of all intermediate products and services that were used to produce the final output.
Reasons for the rising importance of Tertiary sector in India.
(i) This sector provides basic services such as hospitals, educational institutions, post and telegraph services, police stations, courts, municipal corporations, defence, banks, insurance etc. which are basic for the development of the country.
(i) This sector provides services such as transport, trade, storage etc. which help in the development of the agriculture or the Primary sector and the industries or the Secondary sector.
(iii) Increasing income level has created demands for many more services like eating out, tourism, shopping, private hospitals. private schools etc.
(iv) Over the last decade, or so, certain new services such as those based on information and communication technology have become important and essential.
(v) The production of these services has been rising rapidly.
Reasons – Why there is no shift in the share of sectors in employment, as it has been share of sector in GDP
- enough jobs are not created in the secondary and tertiary sector
- Even though industrial output or the production of goods went up by eight times during the period, employment in the industry went up by only 2.5 times.
- While production in the service sector rose by 11 times, employment in the service sector rose less than three times.
- People in the primary sector are underemployment/disguised unemployment. (story of Laxmi)
How to create more employment?
1.Diversification of agriculture (should adopt different types of cultures)
2. Cheap Credits: Government should encourage commercial banks to provide loans to farmers and business at cheaper rates.
3. Provisions of basic facilities : like roads, transportation, banking, market etc. (to link the villages with market)
4. Promoting local and small scale industries.
5. Improvement in Education & health
6. Exploring new sectors for employment
- Planning commission(Niti Aayog) estimates
Education -20lakh jobs can be created in education itself .
Health – More doctors , nurses, health workers are needed.
Tourism – If improved, every year more than 35 lakh people can be employed.
MNREGA (Mahatama Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005)
- enacted on September 2005, based on “right to work”
- State funded work creation programme
- Under MNREGA, all those who are able to and are in need of, work in rural areas are guaranteed 100 days of employment in a year by the govt.
- If govt. fails, will give unemployment allowances to the people
- The work given is related to the land and its productivity.
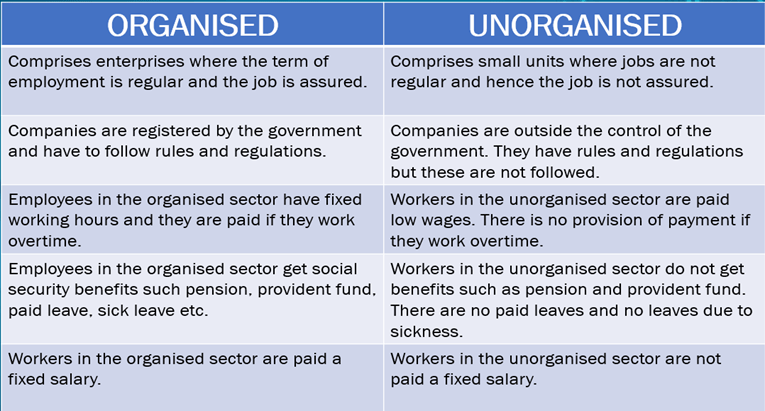
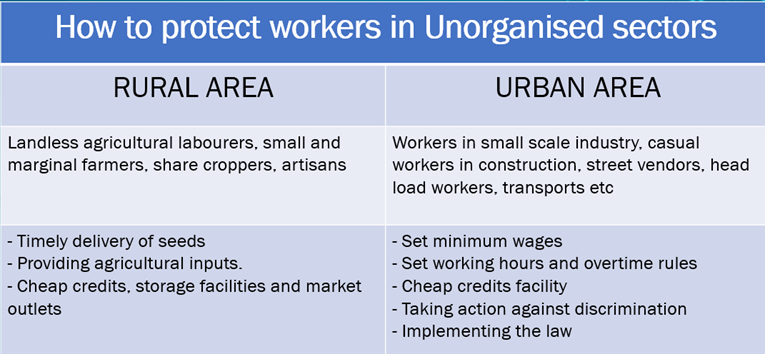
Division of sectors on the basis of working condition
Division of sectors on the basis of OWNERSHIP
| PUBLIC | PRIVATE |
| -Owned by Government – Ex. BHEL, SAIL, IRCTC, BSNL – Motive: Providing Services (Basic needs) Banks, transport, irrigation, electricity, water | – Owned by private individuals and groups – TATA, Reliance, Infosys – Motive: Earn profit |
